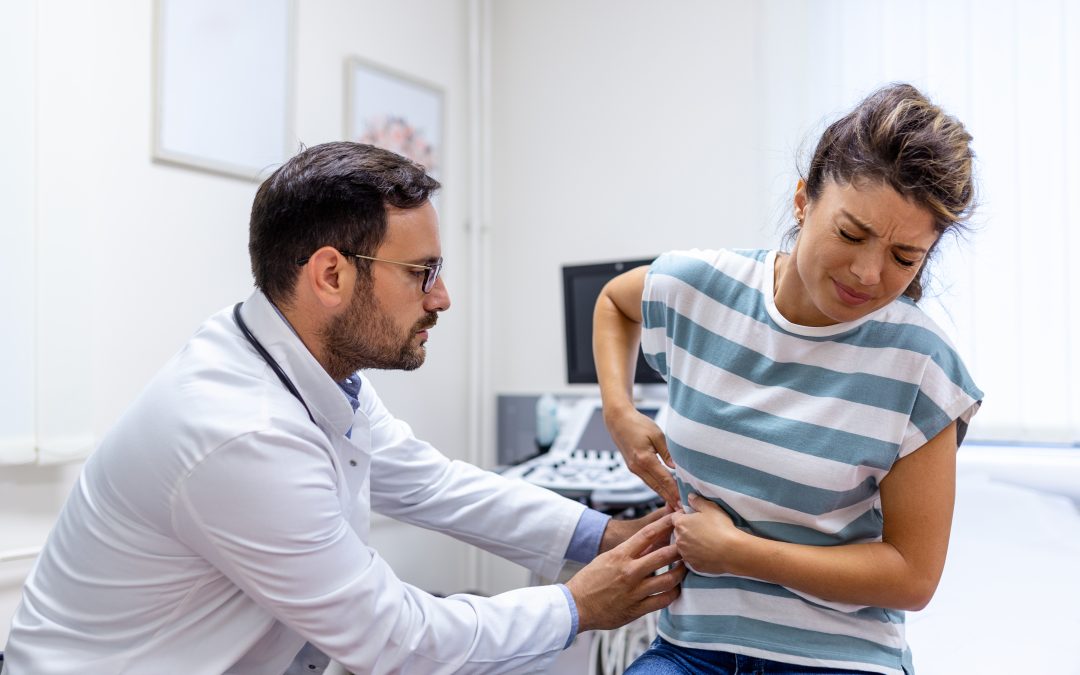
Pyelonephritis is a severe kidney infection that occurs when bacteria travel up from the bladder or urethra and reach one or both kidneys.
This infection can develop suddenly or become chronic if left untreated. People living in Chicago and the surrounding areas often experience symptoms that start mildly but can quickly become severe if left unaddressed.
Pyelonephritis affects the part of the urinary tract responsible for filtering waste from the blood. When bacteria enter this system, they cause inflammation, swelling, and pain. The condition can lead to long-term kidney damage if ignored, which is why early recognition and treatment are vital.
Causes of Pyelonephritis
- An untreated urinary tract infection (UTI) that spreads upward.
- Kidney stones are blocking urine flow.
- Weakened immune system from diabetes or certain medications.
- Pregnancy or anatomical abnormalities in the urinary tract.
Who Is at Risk?
- Women are more prone due to shorter urethras.
- Individuals with chronic bladder infections or those who use catheters.
- Individuals with enlarged prostate or kidney disorders.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Pyelonephritis
The symptoms of pyelonephritis, or kidney infection, often develop suddenly and can vary from mild discomfort to severe illness.
Most people first notice pain in the back, sides, or lower abdomen, which may worsen with movement. This pain typically originates from inflammation in the kidneys as they work to fight off the infection.
Additionally, fever and chills are common because the body is responding to bacterial growth. Many patients also experience frequent or painful urination, similar to a bladder infection, but the discomfort tends to be more intense. The urine may appear cloudy, dark, or have a strong odor, and sometimes contains blood or pus.
Early Symptoms
At first, you may notice discomfort or burning while urinating, similar to a mild UTI. Other early symptoms can include:
- Frequent urge to urinate, even when little comes out.
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
- Mild pain in the lower back or abdomen.
Advanced Symptoms
As the infection worsens, more severe symptoms appear:
- The body’s immune response causes high fever and chills.
- Pain in the side (flank) or back, just below the ribs.
- Nausea and vomiting, especially during fever spikes.
- Fatigue or confusion, particularly in older adults.
When Symptoms Become Dangerous?
At first, you may notice discomfort or burning while urinating, similar to a mild UTI. Other early symptoms can include:
- Frequent urge to urinate, even when little comes out.
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
- Mild pain in the lower back or abdomen.
As the infection worsens, more severe symptoms appear:
- The body’s immune response causes high fever and chills.
- Pain in the side (flank) or back, just below the ribs.
- Nausea and vomiting, especially during fever spikes.
- Fatigue or confusion, particularly in older adults.
If you develop persistent fever, severe pain, or blood in urine, the infection may have spread to your bloodstream — a serious condition called sepsis. Seek immediate care from a Chicago urgent care or emergency clinic to prevent kidney failure.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing pyelonephritis quickly and accurately is essential for preventing kidney damage and other serious complications.
In Chicago medical clinics, doctors start by reviewing your symptoms, such as fever, flank pain, and painful urination, and then confirm the infection through laboratory tests. The first step is usually a urine test, which checks for bacteria, blood, and white blood cells — all signs of a kidney infection.
In more severe cases, doctors may also order blood tests to determine if the infection has spread to the bloodstream.
Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans, can reveal swelling, abscesses, or kidney blockages, which can make treatment more complex. Early diagnosis leads to better recovery and helps prevent recurring infections.
Common Diagnostic Procedures
- Urine analysis: Detects bacteria that cause infection and blood cells.
- Urine culture: Identifies the specific bacterial type to select the best antibiotic.
- Blood tests: Evaluate kidney function and assess sepsis risk.
- CT scan or ultrasound: Check for stones or abscesses that may be causing the blockage.
If you experience persistent pain or unusual urine symptoms, visit a same-day medical clinic in Chicago for proper evaluation. Learn more about infection-related testing in blood tests performed in our lab, or explore how urgent medical attention is for different types of puncture wounds, which also highlights the importance of timely diagnosis.
Pyelonephritis Differs From a Regular UTI
While both urinary tract infections (UTIs) and pyelonephritis involve bacteria in the urinary system, the primary difference lies in the extent to which the disease spreads. A regular UTI usually stays in the bladder or urethra, causing mild burning or frequent urination.
Pyelonephritis, on the other hand, occurs when bacteria move upward into the kidneys, making it a more serious and painful condition. In pyelonephritis, symptoms are not just localized to the bladder — they become systemic, affecting the entire body.
Patients often develop a high fever, flank or back pain, nausea, and vomiting, which are rarely seen with an uncomplicated UTI.
UTI vs. Pyelonephritis
- A UTI affects only the bladder or urethra.
- Pyelonephritis reaches the kidneys, making it far more dangerous.
- UTI symptoms are usually mild, while kidney infection symptoms cause fever, back pain, and systemic illness.
Distinctive Signs of Pyelonephritis
- High-grade fever and chills (rare in UTIs).
- Flank or back pain radiating toward the abdomen.
- Nausea, vomiting, or weakness due to kidney inflammation.
Important to Know the Difference
Understanding these differences helps patients in Chicago seek medical attention sooner. Treating pyelonephritis promptly reduces the risk of hospitalization and prevents chronic kidney damage.
Complications of Untreated Pyelonephritis
When pyelonephritis is not promptly treated, the infection can spread beyond the kidneys and cause serious, long-term health issues.
The most immediate risk is the formation of a kidney abscess, characterized by the development of pockets of pus inside or around the kidneys.
These abscesses can cause severe pain and require drainage or surgery. Another major complication is sepsis, a life-threatening condition that occurs when infection spreads into the bloodstream, leading to dangerously low blood pressure and organ failure.
Possible Complications
- Kidney abscess: A pocket of pus forming inside or around the kidney.
- Sepsis: Infection spreading to the bloodstream.
- Permanent kidney damage: Leading to chronic kidney disease.
- High blood pressure: Due to Scarring and reduced kidney function.
High-Risk Groups
People with diabetes, weakened immunity, or urinary obstructions are more likely to develop complications. Pregnant women should be extra cautious since pyelonephritis can cause premature labor or low birth weight.
When to Visit a Chicago Clinic?
Prompt medical care is crucial to prevent the infection from worsening. Visit a Chicago immediate care clinic or emergency room if you notice symptoms such as:
- High fever that doesn’t lower with medication.
- Persistent back or side pain.
- Blood in urine or a burning sensation while urinating.
- Extreme fatigue, nausea, or confusion.
Doctors may order urine tests, blood work, or imaging scans to confirm the presence of the infection. Early treatment with antibiotics, rest, and hydration often leads to full recovery within one to two weeks.
What to Expect During Treatment?
- Antibiotic therapy to clear infection-causing bacteria.
- Pain relief and fluids to stay hydrated.
- Hospital care is required in severe cases, especially for elderly or diabetic patients.
Treatment and Recovery from Pyelonephritis
Treating pyelonephritis involves removing the infection, alleviating symptoms, and protecting the kidneys from further damage.
Most patients recover well with antibiotics; however, the treatment duration depends on the severity of the infection and whether one or both kidneys are affected. Mild cases can often be treated at home with oral antibiotics, while severe infections may require IV medication or hospital care.
During recovery, doctors recommend staying hydrated, getting enough rest, and avoiding alcohol or caffeine, which can irritate the urinary system.
It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve, as stopping early can lead to a recurrence or antibiotic resistance. For some patients, doctors may schedule a follow-up urine test to confirm that the infection has completely cleared.
Tips for a Smoother Recovery
- Drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria.
- Take antibiotics exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid heavy exercise or lifting during the early stages of recovery.
- Get enough sleep and proper nutrition to boost your immune system.
If you notice symptoms returning after treatment, contact your healthcare provider immediately. For related reading, check what makes same-day medical attention essential for managing health outcomes?

Preventing Pyelonephritis and Protecting Your Kidneys
Prevention is the best defense against kidney infections, especially for individuals prone to recurrent urinary problems. The simplest and most effective way to prevent pyelonephritis is by maintaining good urinary hygiene and hydration.
Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria out of the urinary tract before it reaches the kidneys. It’s also important to urinate regularly and not hold it in, as stagnant urine allows bacteria to multiply and thrive.
Preventive Measures
- Drink plenty of water to flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Urinate frequently and avoid holding it in.
- Wipe from front to back after using the restroom to prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Empty your bladder after intercourse.
- Avoid unnecessary antibiotics, which can disrupt the normal balance of bacteria.
Healthy Kidney Habits
- Maintain a balanced diet low in salt and processed foods.
- Maintain healthy blood sugar and blood pressure levels.
- Get regular checkups if you have recurrent UTIs or kidney problems.
Helpful Information for Kidney and Urinary Care:
Learning about pyelonephritis is just one part of understanding urinary and kidney health. The following internal resources from 1st Choice Med provide additional guidance on recognizing infections, managing related symptoms, and caring for your body after treatment.
These pages offer practical, easy-to-follow medical insights written for patients across the Chicago area:
- How Is Strep Throat Transmitted?
- Signs of Infection After Stepping on a Nail
- How Can Understanding Your Blood Pressure Readings Lead to Better Health?
For More Information:
For medically verified, research-based information about pyelonephritis and kidney infections, visit the Mayo Clinic’s official resource: Mayo Clinic – Pyelonephritis (Kidney Infection).
The Mayo Clinic explains how kidney infections develop, their warning signs, diagnosis methods, and treatment plans. It’s an excellent reference for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of kidney infection care, prevention, and long-term management.
FAQs
1. What is pyelonephritis?
Pyelonephritis is a kidney infection caused by bacteria that travel from the bladder or urethra to the kidneys, leading to inflammation and pain.
2. What are the first signs of pyelonephritis?
Early signs include frequent urination, burning during urination, cloudy urine, and mild back discomfort.
3. How is pyelonephritis different from a regular urinary tract infection (UTI)?
A UTI affects only the bladder or urethra, whereas pyelonephritis reaches the kidneys, causing more severe symptoms such as fever, flank pain, and nausea.
4. Can pyelonephritis go away on its own?
No. This infection requires antibiotic treatment. Untreated pyelonephritis can lead to kidney damage or sepsis.
5. How do doctors diagnose a kidney infection?
Diagnosis often includes a urine test, a blood test, and, sometimes, an ultrasound or CT scan to check for kidney inflammation or obstruction.
6. How long does it take to recover from pyelonephritis?
With proper antibiotics and rest, most patients recover within 7 to 14 days, though severe infections may take longer.
7. Can dehydration cause kidney infections?
Yes. Not drinking enough water allows bacteria to grow in the urinary tract, increasing the risk of infection spreading to the kidneys.
8. Who is at higher risk of developing pyelonephritis?
People with recurrent UTIs, kidney stones, diabetes, or weakened immune systems are more prone to kidney infections.
9. When should I see a doctor in Chicago for pyelonephritis?
If you experience fever, flank pain, nausea, or blood in urine, visit a Chicago urgent care or same-day clinic immediately.
10. How can I prevent pyelonephritis in the future?
Stay hydrated, urinate frequently, maintain good hygiene, and complete all antibiotic courses prescribed for any urinary infection.