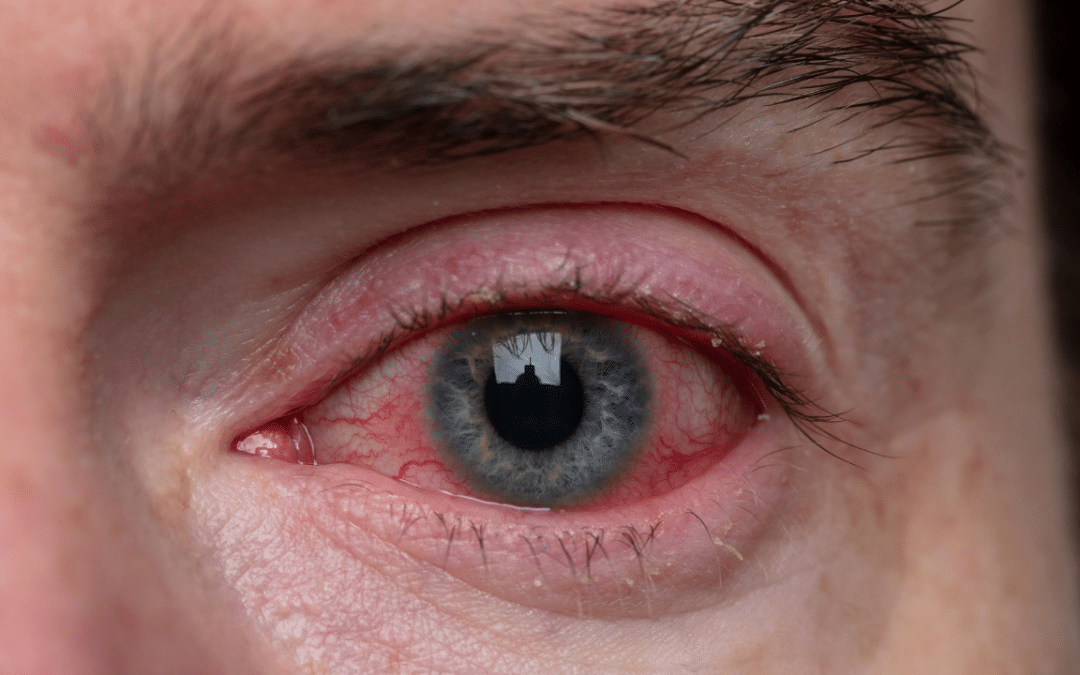
They say the eyes are the window to the soul, but they’re also a window to your health. You’ve likely experienced the discomfort of red, itchy eyes at some point in your life, but it’s crucial to recognize when these symptoms are mere annoyances or signs of something more serious.
As you navigate the complexities of eye health, understanding the top 10 eye infections and their tell-tale symptoms becomes an indispensable tool. From the gritty sensation often signaling conjunctivitis to the sharp pain associated with keratitis, your eyes may be sending you critical warnings that shouldn’t be ignored.
Join us as we unveil these signals, so you can stay vigilant about your vision health and know when it’s time to seek professional care.
Key Takeaways
- Conjunctivitis and stye share common symptoms such as redness, itching, and discharge, but stye is characterized by a painful, red lump and sensitivity to light.
- Proper hygiene, including clean hands and sufficient eyelid hygiene, can help prevent stye formation.
- Warm compresses, gentle washing, and avoiding makeup and contact lenses are effective treatments for styes.
- Keratitis and uveitis both cause inflammation and blurred vision, but uveitis can affect different layers of the eye, and the symptoms vary depending on the type of uveitis.
Conjunctivitis: Common Indicators
If you’re experiencing the hallmark signs of conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, they may include redness, itching, and discharge in one or both eyes. This condition occurs when the conjunctiva, the transparent membrane lining your eyelid and covering the white part of your eyeball, becomes inflamed.
You might also notice a gritty feeling, like there’s something in your eye that you can’t remove. Conjunctivitis can cause your eyelids to stick together when you wake up due to the accumulation of discharge overnight. This discharge can vary from watery to thick and pus-like.
The redness is due to the dilation of small blood vessels within the conjunctiva, which become more visible and give the eye its characteristic pink hue. Itching is a common reaction to the irritation caused by the infection or allergen.
Conjunctivitis can be infectious, caused by bacteria or viruses, or non-infectious, resulting from allergies or irritants. Bacterial conjunctivitis usually leads to more noticeable discharge and may affect only one eye. Viral conjunctivitis often starts in one eye but can quickly spread to the other, while allergic conjunctivitis typically involves both eyes and is accompanied by seasonal allergy symptoms.
Stye: Identifying Signs
You may recognize a stye by a painful, red lump near the edge of your eyelid, often resembling a pimple.
Styes are typically caused by bacterial infection of the oil glands in your eyelids.
Understanding the common symptoms and effective treatments can aid in prompt relief and prevent complications.
Stye Formation Causes
Often caused by a bacterial infection, a stye develops when an oil gland at the edge of your eyelid becomes inflamed. The primary culprit is usually the Staphylococcus bacteria. Understanding the factors that contribute to the formation of a stye can help you prevent this uncomfortable condition.
- Common Causes:
- Touching your eyes with unclean hands, transferring bacteria to the eyelid.
- Using expired or contaminated eye makeup, which can harbor bacteria.
- Obstructed oil glands due to insufficient eyelid hygiene.
It’s crucial to practice good hygiene, avoid sharing personal items like towels or makeup, and to keep your hands away from your eyes to reduce the risk of stye formation. If you wear contact lenses, ensure they’re properly cleaned and handled to prevent bacterial transfer.
Common Stye Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of a stye is crucial for early treatment and relief from discomfort. You’ll typically notice a red, pimple-like bump on the edge of your eyelid, which may cause pain and swelling. A stye often begins with a feeling of tenderness or a small area of inflammation.
As it develops, you may experience increased sensitivity to light, and your eye may water more than usual. Additionally, the affected eyelid may feel heavy or droop slightly.
It’s important to avoid squeezing or attempting to pop a stye, as this can spread the infection. If you observe these signs, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate management and to prevent complications.
Effective Stye Treatments
Once a stye is identified, prompt treatment can greatly alleviate discomfort and expedite healing. Here’s what you can do:
- Warm Compresses
- Apply a clean, warm cloth to the eyelid for 10-15 minutes, 3-4 times a day.
- This warmth helps the stye to come to a head and drain.
- Don’t squeeze or try to pop the stye.
- Cleanliness
- Gently wash the affected eyelid with mild soap and water.
- Avoid using makeup or wearing contact lenses until the stye heals.
- Medications
- Over-the-counter pain relievers can reduce discomfort.
- Topical antibiotics may be prescribed if the stye isn’t improving.
- Steroid injections or surgery are rare options for persistent styes.
Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Keratitis: Symptom Overview
Keratitis can manifest as a painful inflammation of the cornea, the clear front surface of your eye, and may lead to symptoms such as redness, blurred vision, and sensitivity to light. You’re likely to experience a sensation of grittiness or the feeling that there’s something in your eye. This discomfort can be accompanied by tearing or discharge that isn’t typical for you.
You might notice that your eyes become watery or produce a thicker discharge, and your eyelids could become swollen or difficult to open, especially upon waking. Experiencing pain, especially when you look at sources of light, or noticing that your vision seems cloudy or hazy, are signs that shouldn’t be ignored.
If left untreated, keratitis can become severe, potentially resulting in more serious complications such as corneal ulcers, which could threaten your vision. Therefore, if you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. An ophthalmologist can determine the underlying cause, which could range from infection to injury, and provide appropriate treatment to preserve your eye health.
Uveitis: Warning Signals
If you notice unusual redness, pain, or blurred vision in your eye, you may be experiencing early signs of uveitis, an inflammation of the middle layer of the eye. This condition can seriously affect your vision if left untreated and warrants prompt medical attention. Uveitis comes in different forms and its symptoms can vary depending on the type you have.
- Anterior Uveitis
- Symptoms:
- Eye redness and irritation
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Decreased visual acuity
- Intermediate Uveitis
- Symptoms:
- Floaters in the vision
- Blurred vision
- Minimal pain or redness
- Posterior Uveitis
- Symptoms:
- Vision changes, including loss of vision
- Floaters
- Usually less pain than in anterior uveitis
In any case, it’s crucial you don’t dismiss these warning signals. Uveitis can be associated with autoimmune disorders, infections, or can be idiopathic – meaning the cause remains unknown. The treatment often includes anti-inflammatory medication and, in some cases, antibiotics or antiviral drugs if an infection is suspected. You’ll need a thorough examination by an eye care professional who can determine the best course of action for your specific condition.
Endophthalmitis: Symptomatic Clues
When facing the onset of endophthalmitis, you may notice severe eye pain and vision impairment, signaling the need for immediate medical evaluation. Endophthalmitis is a grave eye condition that occurs when the interior of your eye becomes inflamed due to an infection. This inflammation can stem from bacterial or fungal organisms and is often associated with eye surgery, eye injections, or penetrating eye injuries.
You’ll likely experience redness and swelling in the affected eye. The eye might feel tender to the touch, and you could see a discharge. You may also notice that your pupil doesn’t respond normally to light and that the white part of your eye appears red or has pinkish hues.
Light sensitivity is another common symptom, where normal lighting conditions seem intolerably bright. In some cases, you might observe floaters or spots in your vision, which are particularly alarming when they suddenly increase in number or size.
If you experience any combination of these symptoms, especially following an eye procedure or injury, it’s crucial to seek professional medical help immediately. Treatment typically involves prompt administration of antibiotics or antifungal agents and, in certain situations, surgical intervention may be necessary to preserve your vision.
Blepharitis: Diagnostic Signs
As you explore the signs of blepharitis, you’ll find that redness, swelling, and a gritty sensation in the eyes are hallmark symptoms.
Understanding the underlying causes, such as skin conditions or bacterial infections, is crucial for targeted treatment.
Recognizing effective treatments, which can range from hygiene measures to medications, will help you manage this common eyelid inflammation.
Identifying Blepharitis Symptoms
You may frequently experience red, swollen eyelids as a primary indication of blepharitis, a common and chronic eyelid inflammation. This condition can be uncomfortable and persistent, often requiring medical attention for proper management.
Here are key symptoms to look out for:
- Itching or a sensation of burning in the eyes
- Often worsens in conditions of high pollution or allergens
- May intensify after long periods of screen use
- Crusting at the base of your eyelashes
- More noticeable upon waking
- Can cause lashes to stick together or fall out
- Sensitivity to light and blurred vision
- May be accompanied by excessive tearing
- Sometimes, photophobia or difficulty with vision clarity can occur
These symptoms can vary in intensity and may lead to further complications if left untreated.
Blepharitis Causes Explored
Peeling back the layers of blepharitis causes reveals a complex interplay of factors, including bacterial infections, skin conditions such as dandruff of the scalp and eyebrows, and dysfunction of the oil glands in your eyelids. Understanding these causes is crucial to managing your condition effectively.
| Cause Category | Specific Factors |
|---|---|
| Infections | Staphylococcal bacteria, Demodex eyelash mites |
| Skin Conditions | Seborrheic dermatitis (scalp dandruff), rosacea |
| Gland Dysfunction | Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) |
| Allergies | Reaction to eye medications, contact lens solutions |
| Environmental | Chronic exposure to smoke, dust, or chemical irritants |
Each cause requires a tailored approach to treatment. Proper hygiene, medications, or even dietary changes can be part of your management plan. Always consult with an eye care professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment options.
Effective Blepharitis Treatments
Recognizing the various causes of blepharitis sets the stage for exploring the most effective treatments, beginning with recognizing the diagnostic signs that eye care professionals look for. These signs include:
- Lid margin changes
- Swelling or redness
- Crusting at the base of eyelashes
- Misdirected or loss of eyelashes
- Gland dysfunction
- Meibomian glands appearing blocked or altered in function
- Oily or foamy tear film
- Recurrent chalazion or stye formation
- Skin and lash changes
- Scaling or dandruff-like flaking on lashes
- Hyperemic eyelid margins
- Associated skin conditions such as rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis
Your eye care provider may recommend a regimen that includes eyelid hygiene, warm compresses, and possibly antibiotic or anti-inflammatory medications based on these clinical findings.
Dacryocystitis: Recognition Tips
Identifying dacryocystitis involves looking for signs of inflammation in the tear drainage system, typically presenting as pain, redness, and swelling near the inner corner of the eye. You might also notice excessive tearing or discharge, as the infection can block the nasolacrimal duct, which drains tears from the eye into the nasal cavity.
As you assess for dacryocystitis, be aware that the condition can affect just one or both eyes. Press gently on the side of the nose near the affected eye; if there’s a pus-like discharge from the punctum, which is the small opening at the inner corner of the eyelids, it’s a strong indicator of an infection.
Pay attention to any fever or general malaise, as these can accompany the localized symptoms and suggest a more severe infection. In infants, you’re more likely to see a mucus or pus buildup causing a watery, sticky eye.
If dacryocystitis is suspected, it’s crucial to seek prompt medical attention to prevent complications, such as an abscess or cellulitis. Treatment typically includes antibiotics, and in some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to restore proper drainage. Remember, early recognition and treatment are key to avoiding long-term damage to the eye.
Trachoma: Symptoms to Watch
If you’re experiencing symptoms such as itchy, irritated eyes and blurry vision, you may be showing signs of trachoma, a serious infectious disease. Caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, trachoma is highly contagious and can lead to blindness if left untreated.
Pay close attention to your symptoms and seek medical attention if you notice:
- Early Signs
- Mild itching and irritation of the eyes and eyelids
- Increased sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Eye discharge that may contain mucus or pus
- Progression Indicators
- Pronounced swelling of the eyelids
- Blurry vision due to corneal involvement
- In-turned eyelashes (trichiasis), which can scratch the cornea
- Advanced Symptoms
- Severe pain in the eyes
- Clouding and scarring of the cornea, potentially leading to blindness
- Secondary infections from impaired vision
Fungal Infections: Eye Signs
While trachoma is caused by a bacterial infection, various fungi can also lead to eye infections, presenting distinct signs you should be aware of. Fungal infections can be serious and require prompt medical attention to prevent long-term damage. If you’re experiencing any unusual symptoms, it’s important to consult an ophthalmologist.
Here’s a table summarizing common fungal eye infections and their key symptoms:
| Infection Type | Common Symptoms | Affected Area |
|---|---|---|
| Keratitis | Pain, redness, blurred vision, sensitivity to light | Cornea |
| Endophthalmitis | Severe pain, redness, decreased vision, discharge | Interior of the eye |
| Orbital Cellulitis | Eyelid swelling, pain, fever, vision loss | Tissue surrounding the eye |
| Blepharitis | Itchy eyelids, flaky skin, loss of eyelashes | Eyelids |
These infections can be caused by different fungi, including Candida, Aspergillus, and Fusarium species, which can enter the eye through various means, such as injury or contact lens contamination.
It’s crucial to maintain good hygiene, handle contact lenses properly, and seek immediate care if you suspect a fungal eye infection. Early diagnosis and treatment are imperative to avoid complications that can result in vision loss. Remember, these symptoms can mimic other conditions, so a professional evaluation is necessary to determine the correct diagnosis and treatment.
Acanthamoeba Keratitis: Detection Signs
If you experience severe eye pain, redness, and blurred vision, you may be exhibiting signs of Acanthamoeba keratitis, an infection caused by a microscopic organism.
Recognizing the risk factors, such as contact lens wear and exposure to contaminated water, is critical for early detection.
Should these symptoms arise, it’s essential to seek immediate medical attention to prevent potential vision loss.
Identifying Acanthamoeba Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of Acanthamoeba keratitis is crucial, as early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Here’s what you need to watch for:
- Severe Eye Pain
- Notably more intense than typical irritations
- Often accompanied by an unusual sensation of having something in your eye
- Redness and Irritation
- Persistent redness, not relieved by rest or typical over-the-counter remedies
- May affect one or both eyes, depending on exposure
- Vision Changes
- Blurry or hazy vision that doesn’t improve with blinking
- Sensitivity to light, possibly to a debilitating extent
If you experience these symptoms, you must seek medical attention immediately. Acanthamoeba keratitis requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent serious complications, including permanent vision loss.
Risk Factors Exposure
Understanding your risk factors for Acanthamoeba keratitis is key to preventing this severe eye infection. You’re more susceptible if you wear contact lenses, especially if you don’t follow proper hygiene and care protocols. Swimming, showering, or using hot tubs while wearing contact lenses can expose your eyes to Acanthamoeba in the water. Even rinsing your lenses or lens case with tap water increases your risk.
It’s critical you handle your lenses with clean hands and disinfect them as recommended. If you opt for reusable lenses, ensure you replace the lens case regularly. Be aware that homemade saline solutions or reusing disinfectant can also heighten your risk. If you experience eye pain, redness, or impaired vision, seek immediate medical attention, as these could be signs of infection.
Immediate Care Steps
Should you notice any unusual eye discomfort or visual changes, it’s essential to take immediate steps to address potential Acanthamoeba keratitis infection symptoms. Acting swiftly can prevent further complications. Here’s what you need to do:
- Cease wearing contact lenses immediately.
- Remove them with clean hands.
- Don’t reuse or disinfect; discard them.
- Seek professional medical advice without delay.
- Schedule an urgent appointment with an eye specialist.
- Mention any exposure to possible risk factors.
- Initiate basic eye care at home.
- Use prescribed eye drops if available.
- Avoid touching or rubbing your eyes.
These measures are crucial for mitigating the effects of an Acanthamoeba keratitis infection and safeguarding your vision.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How Can Changes in Diet or Nutrition Impact the Prevalence or Severity of Common Eye Infections?
- You’ll find that improving your diet can boost your immune system, potentially reducing the severity and frequency of eye infections by providing essential nutrients that support ocular health and overall immunity.
Are There Any Genetic Predispositions That Increase an Individual’s Risk for Certain Eye Infections?
- Yes, you’ve got certain genes that can up your chances of eye infections. Hereditary factors influence susceptibility, making you more prone to problems like herpetic keratitis or fungal eye conditions.
Can Seasonal Allergies Exacerbate Symptoms of Any of These Eye Infections, and if So, How?
- Yes, seasonal allergies can worsen eye infection symptoms, causing increased itchiness, redness, and swelling, as they amplify your body’s inflammatory response to the infection.
What Role Does Screen Time or Digital Device Usage Play in the Development or Exacerbation of Eye Infections?
- Excessive screen time can strain your eyes, leading to dryness and irritation, which may increase your risk of infections by encouraging you to rub your eyes more often, potentially introducing pathogens.
How Effective Are Natural or Homeopathic Remedies in the Treatment or Prevention of These Eye Infections Compared to Traditional Medical Treatments?
- You’ll find natural remedies less effective than medical treatments for eye infections, as they’re not backed by rigorous scientific evidence and may not target the underlying cause of the infection as precisely.
Statistics
- Eye infections can be spread from person to person through close contact or sharing contaminated objects.
- Eye infections can occur at any time of the year but may be more common during cold and flu season when viruses are more prevalent.
- Good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding touching the eyes, can help prevent eye infections.
- Avoiding sharing personal items, such as towels or eye makeup, can help prevent the spread of eye infections.
- There are many different types of eye infections, including conjunctivitis, stye, and keratitis.
- Eye infections can be more common in people who wear contact lenses, due to factors like improper lens care or extended wear.
- Conjunctivitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or allergies.
- Eye infections can be more common in warm and humid climates, as these conditions create a favorable environment for the growth and spread of bacteria and viruses.
- Using eye drops or artificial tears can help relieve symptoms and soothe the eyes during an eye infection.
- People who work in certain occupations, such as healthcare or childcare, are at a higher risk of developing eye infections due to increased exposure to pathogens.
- In some cases, eye infections can lead to more serious complications, such as corneal ulcers or vision loss.
- Some eye infections can be prevented through vaccination, such as the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
- Regular eye exams can help detect and manage eye infections before they become severe.
- Eye infections are common and can affect people of all ages.
- Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is one of the most common eye infections.
- Using contact lenses properly and following good contact lens hygiene can help prevent eye infections.
External Links
- Mayo Clinic: Keratitis – Mayo Clinic offers comprehensive information on keratitis, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
- CDC: Conjunctivitis Vaccination – The CDC provides information on vaccination for certain causes of conjunctivitis, such as the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
- National Health Service (NHS) – The NHS offers detailed information on conjunctivitis, including common symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
- NCBI: Diagnosis and Management of Bacterial Keratitis – This article on bacterial keratitis offers clinical guidelines for its diagnosis and appropriate management.
- Eye Infection from Contact Lenses – American Optometric Association (AOA) – The AOA provides information on preventing eye infections associated with contact lens wear and proper care techniques.
- Healthline – Healthline provides detailed information on the types of conjunctivitis, including viral, bacterial, and allergic, as well as their respective symptoms and treatments.
- EyeHealthWeb: Pink Eye Symptoms – EyeHealthWeb offers a detailed guide on pink eye symptoms, including common indications of different types of conjunctivitis.
- American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (AAPOS) – AAPOS provides resources specifically focused on conjunctivitis in children, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment.
- AAO: Eye Health Tips for Prevention During COVID-19 – The American Academy of Ophthalmology provides guidance on preventing eye infections, including pink eye, during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Mayo Clinic – Mayo Clinic provides detailed information about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pink eye, a common type of eye infection.
- All About Vision: Corneal Ulcer – All About Vision provides in-depth information about corneal ulcers, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and potential complications.
- AAO: What is Conjunctivitis? – The American Academy of Ophthalmology offers a concise overview of conjunctivitis, including its causes, symptoms, and appropriate treatments.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC provides in-depth information on conjunctivitis, including guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
- Healthline: Keratitis – Healthline’s comprehensive page on keratitis provides information about the different types, causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for this eye infection.
- NCBI Bookshelf: Molecular Pathogenesis of Eye Infections – This book chapter on eye infections from the NCBI Bookshelf offers a scientific overview of the molecular aspects of eye infections.
- AAO: Corneal Ulcer – The American Academy of Ophthalmology offers detailed information on corneal ulcers, a potential complication of certain eye infections.
How To:
How to Recognize and Treat Dry Eyes
Dry eyes can be caused by various factors, including eye infections. Common symptoms of dry eyes include a gritty or foreign body sensation, burning or stinging, redness, excessive tearing, and blurry vision. To manage dry eyes, you can try over-the-counter artificial tears or lubricating eye drops. These products can help alleviate dryness and provide temporary relief. It is important to choose preservative-free options, especially if you need to use them frequently. Applying a warm compress over closed eyes can also help stimulate tear production. Avoiding dry and windy environments, using a humidifier at home, and blinking regularly can also help reduce dry eye symptoms. If self-care measures are not sufficient, or if dry eye symptoms persist or worsen, it is advisable to consult with an eye care professional. They can evaluate your condition, identify any underlying causes, and recommend appropriate treatment options to relieve your dry eye symptoms effectively.